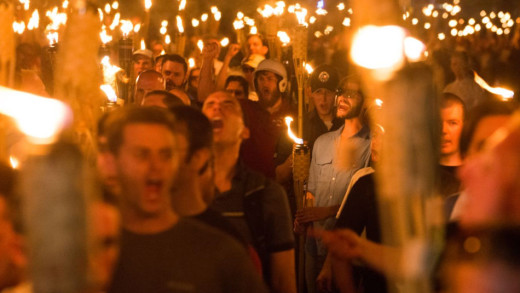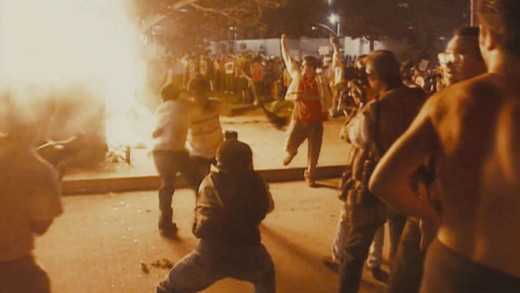Films about police
The murder of George Floyd by police officer Derek Chauvin on May 25, 2020, was arguably a pivotal event in the history of race and policing in the United States. Police on Trial shows, Chauvin’s encounter with Floyd was not the first time the Minneapolis police officer used excessive force on a Black citizen. Nor was it the first time that questions were raised around the culture of the Minneapolis Police Department itself. The film draws on reporting from the Minneapolis Star Tribune, and features never-before-published police cam video of Derek Chauvin using excessive force years before George Floyd’s death, to document the trial and murder-conviction of Chauvin, and the various responses for police accountability and reform in Minneapolis.
Following the police shootings of Bernardo Palacios Carbajal and George Floyd in the United States, Shots Fired investigates the use of deadly force by police in Utah, with local journalism partner The Salt Lake Tribune. The filmmakers are given rare behind the scenes access to police training, and in the police’s bid to smooth public perceptions, access to discuss tactics and accountability, as well as racial disparities in the way force is used. The film pieces together data and videos from police ‘use of force’ cases, and asks the hard questions about police culture in the United States in general.
All Light, Everywhere is an arthouse film that traverses the biases of how we see things, told through the use of police body-worn cameras from the Axon corporation. As such surveillance technologies become a fixture in everyday life, the film interrogates the myth of an objective point of view, probing the biases inherent in both human perception, the lens, and the culture driving the surveillance machines—asking what it means to look and see, but also what is not viewed, and the power imbalance of whom watches whom. Through provocative vignettes, the film provides space to dismantle the perpetual insistence that if everything was recorded and processed by purportedly “neutral” sources, then both criminal activity and authoritarian malfeasance would be reduced.
During the 2019–2020 Hong Kong protests, after 6 months of ongoing actions, and with protesters facing escalating stakes from police shootings and other violent repression, students began to fortify a number of the city’s major universities and occupy vital roads nearby. This lead to a peak moment in the protest movement—the siege of the Hong Kong Polytechnic University. Protesters gathered at the university to defend their roadblocks, while the police shot tear gas and used water cannons to shower the protesters with water containing blue colouring and chemical irritants. 1,458 canisters of tear gas were fired at protesters, as well as 1,391 rubber bullets, 325 bean bag rounds, and 256 sponge grenades. The city’s hospitals were overwhelmed by the number of protesters needing urgent medical attention. Burn with Us documents a first-hand view of the conflict, and its results, in a fly-on-the-wall style.
What does it mean when so-called Artificial Intelligence systems increasingly govern all of our civil rights and social interactions? What are the consequences for the people AI systems are biased against? When MIT Media Lab researcher Joy Buolamwini discovers that many facial recognition technologies do not accurately detect dark-skinned faces nor properly detect the faces of women, she delves into an investigation which reveals widespread bias in the algorithms that already drive much of the modern world. As she uncovers, these systems are not neutral, and are already having severe social and political impacts. Coded Bias documents this investigation, and the women who are leading the charge to ensure civil rights are protected from the relentless inertia of technology.
The Monopoly of Violence is a study of police brutality in France, specifically documenting the gilet jaunes protest movement of 2018 and 2019. But the footage could just as easily have been from the United States, or Hong Kong, or Britain. Citing the work of sociologist Max Weber as a starting point, which shows that the state has the monopoly on the legitimate use of physical force, the film expands into the space of questioning a form of policing that descends into systematic brutality and violence. Using footage from demonstrators and independent journalists to ground the analysis, the images are discussed between lawyers, representatives of social movements, academics, police officers, and victims of police aggression. The result is a clarion call for the rights of the citizen, and the accountability and responsibility of the State.
In 2015, Sandra Bland, a politically-active 28-year-old black woman from Chicago was stopped by police for a minor traffic offence in a small Texas town. Three days later, she was found dead in a police cell. Though the state claimed it was a suicide, her death enraged the public amid allegations of racially-motivated police murder. This film begins in the days after Sandra’s death, tracking the ensuing two-year battle between Sandra’s aggrieved family and the State of Texas. Following the details about the case, Say Her Name is punctuated by Sandra’s own passionate and moving commentary in 30-second “Sandy Speaks” video blogs. We see an empowered, enlightened woman, whose sharp, humorous, charismatic remarks address subjects from educating kids about black history to police brutality to the importance of natural hair. Say Her Name takes viewers inside this story that galvanised activists across the United States and the world.
Investigate journalist A.C. Thompson reports on the background of the white supremacists and neo-Nazis involved in the “Unite the Right” rally in Charlottesville, 2017. The event itself was chaotic and violent, amidst a backdrop of general passivity by the police and supine intelligence agencies, peaking on the day with a self-identified white supremacist ramming his car into a crowd of protesters, killing a young woman, Heather Heyer, and injuring 19 other people. Documenting Hate contextualises the events of that day by looking at the renewed trajectory of fascism in the United States, and the kinds of people attracted to its place in modern times, while profiling some of the characters from Charlottesville that lurked in the background. The second part of the investigation deals with the wake of the deadly anti-Semitic attack at the Tree of Life synagogue in Pittsburgh, showing how a neo-Nazi group, Atomwaffen Division, has actively recruited inside the United States military.
In 2015, peaceful protests and destructive riots erupted when Freddie Gray, a 25-year-old African American, died in police custody in Baltimore, United States. While the city waited to see the fate of the six police officers involved in the incident, who were all ultimately not punished, Baltimore Rising shows activists, police officers, community leaders, and gang affiliates, who struggled to hold the city together, as the homicide rate hit record levels. The death of Gray by police catalysed the longstanding fault lines in a distraught community, damaged by corruption and inequality. Baltimore Rising chronicles the determined efforts of people on all sides who are working to make their community better, sometimes coming together in unexpected ways.
Do Not Resist documents, from the perspective of the police, their view of the social unrest following the shooting and killing of Michael Brown by police in Ferguson, 2014, against a backdrop of the routine and escalating use of military tactics and high-powered weaponry by local police forces throughout the United States in the past two decades. Military equipment deployed throughout the Middle East returns home to be used against the citizenry. Local police recruitment and training is awash in military commandments backed by views of escalating ‘righteous’ violence and sadism. Meanwhile curfews are imposed, along with frivolous drug raids and incessant racial profiling. The voices of concerned citizens ignored. What is the cultural and technological trajectory here?
Consisting entirely of archival footage, LA ’92 chronicles the 1992 Los Angeles riots, 25 years after they have passed. It includes film and video from the 1965 Watts Riots, the 1973 election of Tom Bradley, the 1978 promotion of Daryl Gates to Chief of LA Police, the shooting of Latasha Harlins, the Rodney King videotape, and the subsequent riots and violence that erupted after the acquittal of the officers involved in King’s beating.
Let It Fall: Los Angeles 1982–1992 is a deep examination of a tumultuous decade in the city of Los Angeles, United States, leading up to the events of April 29, 1992, when the verdict was announced in the Rodney King case. The film traverses the conflicts between law enforcement and the black community to look at tensions across the city as a whole, and traces the roots of civil unrest to a decade before uprisings, as told through interviews with eyewitnesses and people directly involved in the events from diverse neighbourhoods across the city, including black, white, Hispanic, Korean, and Japanese Americans.
Told by the activists and leaders who live and breathe for justice, Whose Streets? is an unflinching look at the uprising in Ferguson in the United States after unarmed teenager Michael Brown is killed by police and left lying in the street. Grief, long-standing racial tensions, and renewed anger bring residents together to hold vigil, and protest the latest tragedy in a long history of police brutality. Empowered parents, artists, and teachers from around the country come together to act and support. As the national guard descends on Ferguson with military grade weaponry, young community members become the torch-bearers of a new generation of resistance. Whose Streets? is a powerful battle cry from a generation fighting, not only for their civil rights, but for the right to live.
Copwatch depicts WeCopWatch, an organisation dedicated to video recording the police in the United States. For example, Cop Watch members capture original video of the deaths of Eric Garner in Staten Island and Freddie Gray in Baltimore. Its members legally record and document police arrests as part of a movement for police accountability and transparency, but often find themselves to be the victims of chaos and police brutality as a result of the culture of extreme police misconduct and violence. The stories are told through Ramsey Orta, Kevin Moore, who filmed the police abuse of Freddie Gray, and David Whitt who lived in the apartment complex where Michael Brown was killed, as well as Jacob Crawford, who co-founded Copwatch groups inspired by the Berkeley Copwatch group. The film shows how Cop Watchers are dedicated to bringing awareness to their community, by exposing police brutality and harassment.
The setting is in the current and ongoing troubling police culture of violence, profiling and racism. Even a former NYPD officer now breaks ranks to say that the force aggressively targets poor and minority communities in order to meet secret and illegal arrest quotas. The result is a level of systemic harassment and brutality that could be hard to demonstrate, if not for growing groups of Cop Watchers—everyday citizens wielding cameras, that routinely record and publish troves of evidence documenting all kinds of patterns of police brutality and misconduct. This film follows some of the people who are doing this work, and clearly the police don’t like it. They push back hard. Cop Watchers hence face long prison sentences and trumped up charges for simply recording the police—something that is not itself a crime. In an age of intense corruption of public institutions, this film lays out abuses of power on a frightening scale, showing just how urgent serious action is required if a free society is said to continue to exist.
The Bentley Effect recounts the story of citizens throughout the Northern Rivers shire of Australia protesting against coal-seam gas extraction. When the community first learns of the news, a critical mass of people from all walks of life—farmers, landowners, mums, dads, activists, and scientists—come together to rally against the invasion. But despite enormous public opposition, the gas industry and the State Government are determined to see their plan through. So the community changes tact and resorts to differing methods of civil disobedience and non-violent protest. This culminates in a music festival of sorts in Bentley, New South Wales, which brings together the community and also spurs them on to initiating political action.
Audrie & Daisy is a documentary about the trend of teenage girls in the United States being sexually assaulted by their male classmates, and having the assaults recorded and shared on social media. It looks at the trend that the legal system tends to systematically minimise and dismiss cases, resulting in victimised girls not receiving justice. Girls often end up getting bullied both in school as well as online for being rape victims, and the pictures and videos are posted online—almost as trophies—by teens that have committed and witnessed these crimes. The online forum for sharing these images and comments has become the new public square of shame for adolescents. Audrie & Daisy aims to shed light on this dark corner of life facing young adults, and serves to form a powerful tool for honest conversation, analysis, and real justice.
Over the past several years, a seemingly relentless string of killings by police of unarmed black men—Michael Brown in Ferguson, Freddie Gray in Baltimore, Eric Garner in New York—has reignited issues around race, policing and civil rights in the United States that have been languishing unresolved for decades. Recently the issues are critical enough that the Department of Justice has stepped in to mandate reform of several police forces renowned for brutality and institutional abuses of power. In Policing the Police, journalist Jelani Cobb gets up close and personal with police departments and officers alike, to show from the inside the difficulties these institutions now face of fixing a broken relationship with the community after decades of mistrust. Is it even possible with the current police culture? Policing the Police is a powerful case study of these questions, and a light on just how much has to change.
Arresting Power documents the history of conflict between the Portland police and members of the community throughout the past fifty years in the United States. The film portrays personal stories of victims of police misconduct, the families of people who were killed by police, and members of community activist groups working for reform and abolition. Using experimental filming techniques, meditative footage, and official police radio audio feeds, Arresting Power pieces together a space for understanding a lens on the impacts of police violence and community attitudes.
Peace Officer explores both the militarisation and increasingly violent culture of police forces, as told through the career of William Lawrence, a former sheriff of Davis County in Utah United States, who established and trained the state’s first SWAT team. As a gifted investigator, Lawrence’s savvy skills help break the Ted Bundy case. He also sees SWAT enter the public consciousness and transform the culture of policing throughout the 1970s, along with the convergence of the War on Drugs on policing attitudes and police violence. He eventually leaves public office, concerned, when soon after, his son-in-law is killed in an emergency call gone awry by the very same SWAT unit he created 30 years ago. An internal investigation of course finds no police wrongdoing, so Lawrence turns to his own renowned investigative skills. He sets out to not only uncover the truth of his son-in-law’s homicide, but to tackle the culture and attitudes of modern-day policing on a national level.
In the early 2000s, two brothers garnered tremendous wealth when they started a company selling so-called “non-lethal” taser weapons, which quickly saturated police agencies and reinforced a culture of trigger-happy police officers. But instead of “saving lives” as was the catch-cry of the taser, and the company, the weapons were instead commonly used for pain compliance, and lead to a spurious string of deaths. The company didn’t back down. They insisted, despite mounting evidence to the contrary, that their weapon was safe and not at fault—not even a contributing factor—in the killings. Killing Them Safely delves into this troublesome mindset and that of the company, as well as the social implications of such weapons in a problematic police culture.
Filmed over 18 months, Lessons in Dissent is a kaleidoscopic portrait of a new generation of Hong Kong democracy activists. 18-year-old Joshua Wong dedicates himself to stopping the introduction of National Education. His campaign begins to snowball when an interview goes viral on social media. With the new school year fast approaching, a showdown with the government seems inevitable. So with a microphone in hand, and still in his school uniform, he takes to the streets to protest, along with 120,000 people in support. Meanwhile, former classmate Ma Jai fights against political oppression on the streets and in the courts. Having dropped out of school and dedicated himself to the movement, he endures the persecution suffered by those not lucky enough to be protected by the glare of the media. Lessons in Dissent catapults the viewer on to the streets of Hong Kong, confronting the viewer with the country’s rising energy of dissent.
The legacy of the Bush administration and the so-called “War on Terror” includes a new logic that stretches well beyond the realm of overzealous security agencies, airport security and international relations, and into suppressing public protest; expanded surveillance aimed at entire populations, but especially activists; and mobilising fear for social control. Special police techniques have even been developed and applied in order to specifically suppress dissent and manage protests, especially in the wake of the rising anti-globalisation movements towards the turn of the millennium. Preempting Dissent provides a quick overview of how some of this logic developed, as well as a glimpse of how political protest in the West has been shaped and controlled in the “post-9/11″ years, up to and including the so-called Occupy movement. By provoking a reflection of the implications of the logic of the “War on Terror” and how its applied to stifle political protest, Preempting Dissent aims to lay some of the groundwork to develop more effective resistance tactics.
How To Stop A Multinational follows three women in Argentina as they put themselves in harms way to stop a gold mining company from entering their town. With the activists having defeated a Canadian mining company, the campaign is now against a Chinese one that wishes to extend the operation, making use of large quantities of fresh water—up to 45,000,000 litres per day—a plan that seriously threatens the future viability of the town and the environment. This short film documents the campaign which is still in its early days, where activists carry out a series of direct-actions to stop the mining company from physically entering the town; training villagers, informing others and filming the outcomes along the way…
Peter Francis, a former undercover police spy turned conscientious whistleblower, breaks ranks by speaking to the media after becoming troubled by the unaccountable culture of secret police operations throughout the United Kingdom targeting peace activists for decades. Tactics included undercover police officers having sexual relationships with activists, even going as far as commonly having children with the women they were spying on. Undercover agents also often assumed the identities of dead children in order to have “solid cover stories.” We also see how undercover police were asked to look for intelligence that could be used to discredit the family of murdered teenager Stephen Lawrence and their campaign. The Lawrence family both speak of their shock at hearing about that the police did this to them. This short investigation opens a flood of questions about the secret history of covert police operations, and indeed the future of them in the context of the sprawling surveillance state of today.
In the spring of 2012, a massive student strike in opposition to a tuition hike, rocked the streets of the Montréal for over six months. Protests and mass direct-action on the street became part of daily and nightly reality. Several times during the tumultuous spring, the numbers in the streets would reach over one hundred thousand. Police routinely clubbed students and their allies, and arrested them by the hundreds. Some were even banned from entering the city. But every time the cops struck, the student movement got bigger and angrier. This is a story about how the arrogance of a government underestimated a dedicated group of students, who through long-term organising, laid the foundation for some of the largest mass demonstrations in Canada’s history.
Let the Fire Burn documents the conflict of the City of Philadelphia and the Black Liberation organisation MOVE, that led to a disastrously violent confrontation in 1985. MOVE was originally established as a “back to nature” movement that practised green methods, and in May 1985, the Philadelphia Police Department decided to take action to evict the group from their row house at 6221 Osage Avenue. When gunfire broke out and tear gas was not enough to pull the MOVE members out of the house, the police decided to drop explosives on the house. A fire soon began to blaze, endangering the several children now trapped inside the house. In a controversial decision, the police opted to let the fire burn, resulting in the destruction of over 60 homes and the death of five children and six adults. Eleven people died in the resulting fire, and more than 250 people in the neighbourhood were left homeless. Ramona Africa, one of the two survivors, said that police fired at those trying to escape. The investigation commission that followed found that city leaders and law enforcement had acted negligently, but no criminal charges were filed.
Less than three years after a popular uprising that led to President Hosni Mubarak’s ousting, and just one year after Egypt’s first elections, the elected government has been overthrown and the Egyptian military is running the state. And the Muslim Brotherhood—the secretive, long-outlawed Islamist group that came out of the shadows to win the presidency in June 2012—is once again being ‘driven underground.’ Were the Brothers ever really in charge? Or was the Egyptian deep state—the embedded remnants of Mubarak’s police force, Supreme Court and, most of all, military—in control all along? In Egypt in Crisis, we go inside the Egyptian revolution, tracing how what began as a youth movement to topple a dictator evolved into an opportunity for the Muslim Brotherhood to seemingly find the political foothold it had sought for decades—and then why it all fell apart. With Egypt’s hopes for democracy in tatters, and the military-led government violently cracking down, what will happen next?
During the summer of 2013, a new area of occupied Sápmi (the northern parts of Fennoscandia in Europe) were under attack from the mining industry. If it were not for groups of brave resisters, the test blasting outside Jokkmokk in Lapland, Sweden, would have gone by without incident. The local Sámi people would have once again been exploited, and future generations poisoned without even a debate. But this time, something happened. The Gállok Rebellion tells the story of the resisters in Gállok, and shines a light on views which are not often televised. The film collates the efforts of many groups working together and serves as a call to action, to continue to protect the natural world which is under siege.
Perfect Storm offers an initial analysis of the underlying causes and wider context surrounding the riots throughout England in 2011. Contrary to the portrayals presented by mainstream media and trite political rhetoric around law and order, the riots were sparked by poverty, inequality and frustration over police killing a young man in Tottenham. How does the damage weigh up to the criminal conduct of banks and corporate tax avoiders when the costs of the riots are over four thousand times less than the recent financial crisis? Whose priorities are at play here?
Just Do It — A Tale of Modern-Day Outlaws follows a group of activists in the UK to document their protests and actions over one year dealing with issues around climate change. Demonstrations at Copenhagen’s 2009 G20 summit and at the Drax coal power station in North Yorkshire, England, are just some of the events documented.
In June 2010, leaders from the twenty largest economies met in Toronto, Canada with representatives of corporate interests to discuss the policies that shape globalisation. With exclusion zones, overlapping layers of security fencing and an estimated 25,000 police and military personnel, the city was transformed into an armed grid. Over 1.3 billion dollars were spent on security measures — more than all previous G8 or G20 meetings combined. Tales From The G20 shows some sides of the Summit, from unmarked vans with snatch squads of plainclothes police to the pre-emptive arrest of people now facing years in prison for organising demonstrations or simply being on the street…
Mark Kennedy was an undercover police officer who spent eight years as a infiltrator and informer on environmental movements and other protest groups throughout Europe. Confessions of an Undercover Cop accounts the actions of Kennedy from his perspective, which reveals an insight into the dark, twisted psychology of a police informant and the methods they use to destabilise movements and activists…
By examining the modern culture of industrial civilisation and the persistent widespread violence and environmental exploitation it requires, END:CIV details the resulting epidemic of poisoned landscapes and shell-shocked nations, while further delving into the history of resistance and the prospect of fighting back against such abuse. Detailed is an overview of the environmental movement analogous with the historical whitewashings of the supposedly ‘pacifist’ social struggles in India with Gandhi and Martin Luther King in the United States; the rise of greenwashing and the fallacy that all can be repaired by personal consumer choices. Based in part on ‘Endgame,’ the best-selling book by Derrick Jensen, END:CIV asks: If your homeland was invaded by aliens who cut down the trees, poisoned the water, the air, contaminated the food supply and occupied the land by force, would you fight back?
On October 15th 2007, a series of intense police raids occurred around the small village of Ruatoki in New Zealand. Operation 8, as it was called, was the result of 18 months of invasive surveillance of Maori sovereignty and peace activists accused of attending ‘terrorist training camps’ in the Urewera ranges—the homeland of the indigenous Tūhoe people. This film examines why and how the raids took place. Did the “War on Terror” become a global witch-hunt of political dissenters reaching even to the South Pacific?
The Tall Man is the story of an Aboriginal man, Cameron Doomadgee (tribal name: Mulrunji) who in 2004 was arrested by Senior Sergeant Chris Hurley (the so-called ‘Tall Man’) in Palm Island, a tropical paradise in Australia’s Far North. 45 minutes after the arrest, Mulrunji was found dead in the Palm Island police station. His injuries were like those of someone who’d been in a fatal car crash. The police claimed he had “tripped on a step,” but the community knew this was bullshit. The Palm Islanders protested for truth and burnt down the police station. The subsequent trial of Hurley—who had been decorated for his work in Aboriginal communities—made headlines day after day, shadowed by Queensland police threatening to strike. The police officer was acquitted for the death by the Attorney General. The Tall Man follows these stories by delving into the courtroom, the notorious Queensland police force, and speaking with the Indigenous community of Palm Island, where this tale is sadly still indicative of many of the continuing atrocities of Aboriginal deaths in police custody.
A secret illegal project from the 1950s, 60s and 70s called COINTELPRO, represents the state’s strategy to prevent resistance movements and communities from achieving their ends of racial justice, social equality and human rights. The program was mandated by the United States’ FBI, formally inscribing a conspiracy to destroy social movements, as well as mount institutionalised attacks against allies of such movements and other key organisations. Some of the goals were to disrupt, divide, and destroy movements, as well as instilling paranoia, manipulation by surveillance, imprisonment, and even outright murder of key figures of movements and other people. Many of the government’s crimes are still unknown. Through interviews with activists who experienced these abuses first-hand, COINTELPRO 101 opens the door to understanding this history, with the intended audience being the generations that did not experience the social justice movements of the 60s and 70s; where illegal surveillance, disruption, and outright murder committed by the government was rampant and rapacious. This film stands to provide an educational introduction to a period of intense repression, to draw many relevant and important lessons for the present and the future of social justice.
With economic collapse besieging the United States, domestic violence statistics show a sharp increase in violence against women. States are closing shelters and cutting support programs, and the culture ignores domestic violence, except when celebrities are involved on TV. In the meantime, more spouses have been killed by their partners in the past several years than soldiers have been killed in Iraq. Power and Control addresses this life and death issue during a time of urgent crisis, a timely and comprehensive exploration of physical and emotional abuse in dominant culture, as refracted through the story of Kim Mosher, a mother of three who has recently left her abusive husband. As Kim and her fragile daughters take up residence in a domestic violence shelter, the film follows the harrowing struggles in a single-parenting survivor’s quest to find work, housing and peace of mind. We also meet Kim’s husband, Josh, himself a survivor of abuse. His attempts to explain his behaviour are troubling—shocking in the context of the story’s final twist. The multi-level narrative also examines the root causes of domestic violence and the solutions that have evolved to stop it, celebrating the battered women’s movement activists who demanded revolutionary change in the 1980s, and examining alternative approaches now being advocated.
The Chicago Conspiracy reviews the legacy of the military dictatorship in Chile by sharing the story of combatant youth who were killed by the Pinochet regime as a backdrop to the history of the military dictatorship and current social conflict. The larger history is wrapped around three shorter pieces, which explore the student movement, the history of neighbourhoods that became centres of armed resistance against the dictatorship, and the story of the indigenous Mapuche…
Lethal Force takes a detailed look at four incidents, in different parts of Australia, where people suffering mental illness or psychological distress died after being shot or tasered by police. Specifically detailed is how in certain cases, the victims had even sought help at hospital and after having left of their own free will, were shot dead by police…